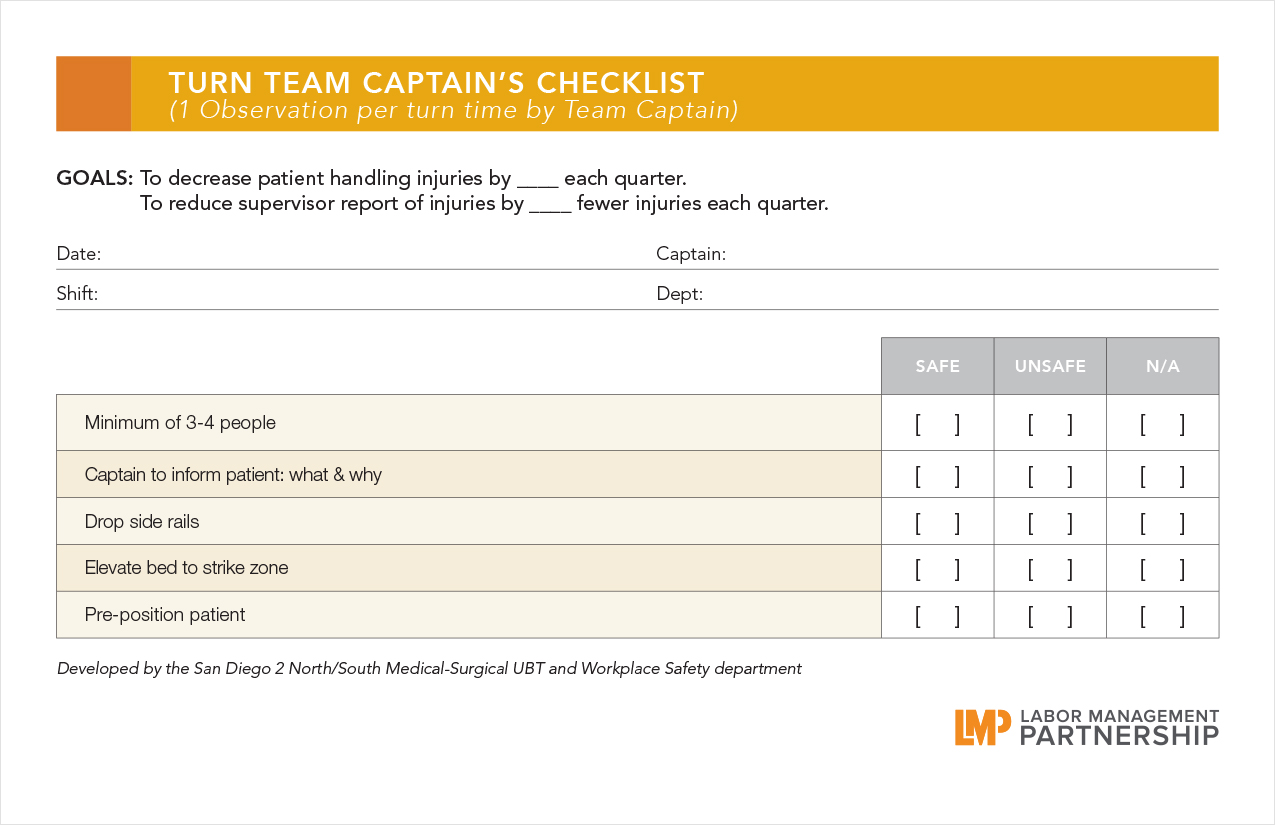
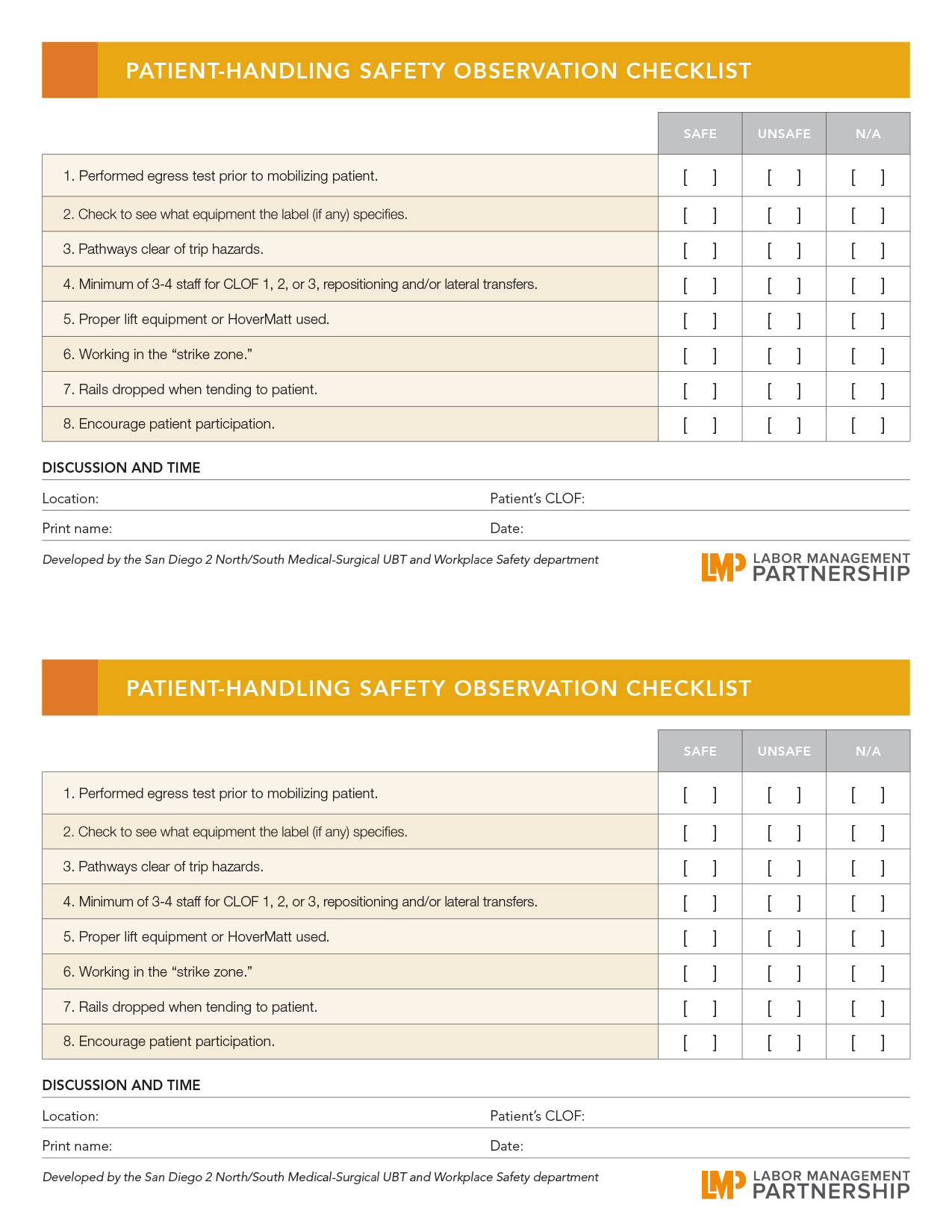
When Helen Bevan told her National Health Services colleagues in the United Kingdom she would be speaking at a conference of Kaiser Permanente union employees, they were surprised.
“What could they possibly learn from us?” they asked.
A lot, she says.
“Kaiser is a role model for us,” explains Bevan, chief of service transformation at the NHS Institute for Innovation and Improvement, part of the largest government-sponsored health care system in the world.“We look at and learn a lot from Kaiser in terms of innovations, efficiencies, use of new technology and its approach to patient care.”
We have much to learn from them as well—especially when it comes to large-scale change.
How to move forward
“To move forward in health care, leaders must tell their story, make it personal, create a sense of ‘us’ and include a call for action,” says Bevan, one of the plenary speakers at this year’s Union Delegates Conference in Hollywood. “The way to build and sustain health care reform is to learn the lessons of social movement leaders.”
Bevan’s point is on the mark. The 700 delegates attending the conference, themed “You Gotta Move,” were called to act on improving their own health and the health of their communities. They took that message to the streets of Hollywood, distributing fliers with tips on easy steps to take to improve health. Some also gathered for a flash mob in front of Hollywood’s Grauman’s Chinese Theatre, dancing to Beyonce’s “Move Your Body”—a song made for Michelle Obama’s “Let’s Move” campaign to end childhood obesity.
“It’s such a great experience to see the extent to which union members are stepping up to be a part of the change process,” Bevan says.
Building commitment and energy
The actions at the delegates conference—and beyond—are precisely what’s needed to reform health care in America and the world, she says, adding: “We can only create large-scale change if we build a platform of commitment and energy.”
Because unit-based teams, KP’s platform for improvement, engage frontline workers, managers and physicians, they “already have that commitment and energy,” Bevan says. UBTs “create a sense of coming together around a common cause and achieving the same outcomes.”
But UBTs alone can’t bring about the large-scale change needed to meet the unprecedented challenges to improve quality and reduce costs.
Engage and inspire
“Transformation needs to occur at all levels of the organization in order for it to be sustainable,” Bevan says. “Senior leaders need to stop being pacesetters and start engaging, inspiring and emotionally connecting with employees. The passion is there. We just have to tap into it.”
As the task of delivering health and health care becomes more complex and the scale of change increases, “We need to think widely and innovatively about how we define the role of senior leaders,” Bevan says.
That’s where social movement thinking comes in. “Successful movements often have charismatic leaders—think Martin Luther King or Nelson Mandela—but what ultimately guides and mobilizes the movement are leaders at multiple levels.” The key, she says, is to depend less on reorganizing structures and processes as the catalyst for change and more on unleashing emotional and spiritual energy for change.
“People are much more likely to embrace change if it builds on the passion, the sense of a calling that got them into health care in the first place,” Bevan says. By connecting to that shared passion through storytelling, “We can create an unstoppable force for change.”